

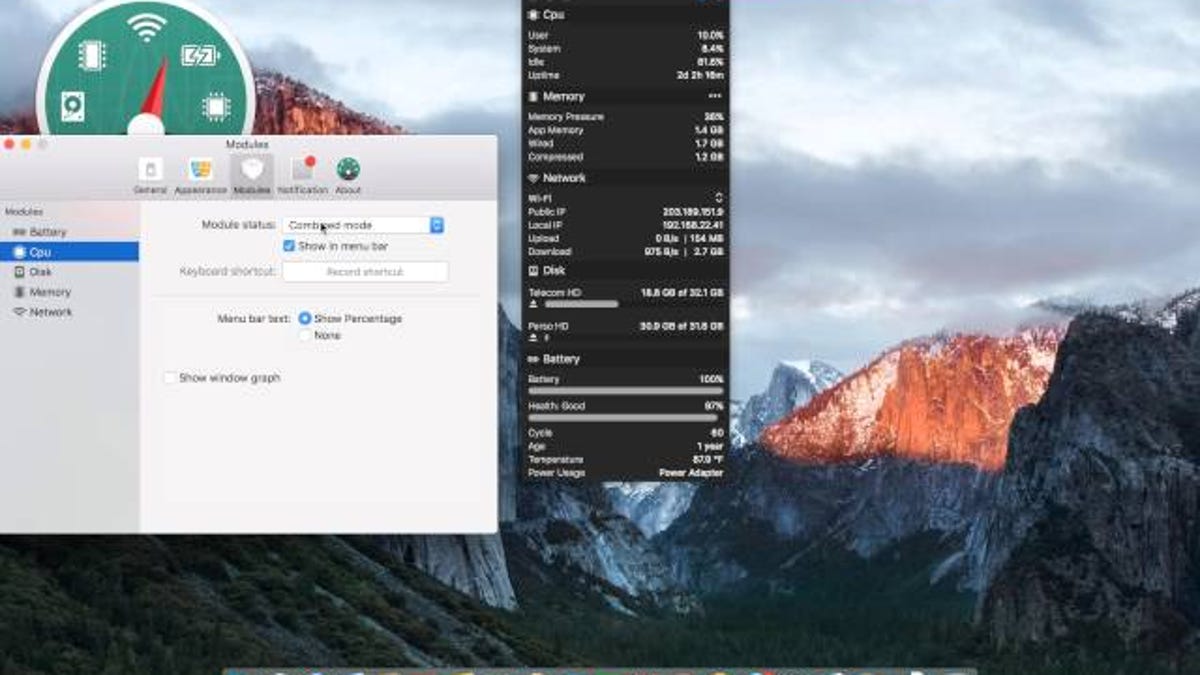
Similar to the Test Info pane, the Service Info pane enables you to change the services - and lets you auto-pause a service, affecting all tests that use that service.īut what about websites that have banners or other irrelevant content? Won't that confuse Simon into thinking the page has changed? Nope! Simon has a very useful feature called Filters, where you can tell it what part of the page to look for, e.g. Not a problem! You can customize the services to edit the defaults for the built-in ones, or even add new ones. Usually the built-in services are ample, but what if you want to delve deeper? Sometimes you have a special requirement and want to check some other kind of server.
Web Page: Check a website for changes or failures. TCP Port Scanner: Checks the status of all TCP ports on a server. SSH: Converse with a remote secure shell session. System Error Log: Results in a failure if a specified error message occurs in today's system.log. SNMP Status: Checks the status of a SNMP-connected device it's a failure if it is not up. Screenshot: Takes a screenshot whenever the test is checked. Samba SMB: Checks that a Samba SMB client is online and responding. Port Available: Like the Port services, but simply checks if a port is open, without actually communicating on it. Ping: Ping any server to check responsiveness you can specify timeout and packet loss limits. Outgoing Mail (SMTP): Outgoing mail usually goes via a SMTP server make sure it is available (plus a SSL variation). Network Time (NTP): Checks that a network time server is responding. Incoming Mail (POP): Another kind of mail server (plus a SSL-enabled edition is also available). Incoming Mail (IMAP): Communicate with an IMAP mail server, to make sure it is available, and/or look for new messages. FTP: Look at a file on an FTP server, to detect its availability or changes. Drive Status: Checks the drive capacity threshold, S.M.A.R.T. DNS: Query a domain name server to ensure the domain is visible. Application: Make sure an application is present, and optionally running - can re-launch if not via Launch notifier. For example if you know that a server will be unavailable, perhaps during a periodic reboot or regular maintenance, or you simply don't want to know about changes at certain times, like of a blog when you should be working.  The Auto Pause page enables you to tell Simon not to check on specified days or time intervals. The Reports page specifies whether the test should appear on some or all reports.
The Auto Pause page enables you to tell Simon not to check on specified days or time intervals. The Reports page specifies whether the test should appear on some or all reports. #MAC OS SYSTEM MONITOR HOW TO#
The Notifiers page can be used to indicate how to alert you when a change is detected, if the service goes down, recovers from a failure, or if a filter detects a problem.You can easily tell the test to ignore parts of the service output, concentrate on just the area that interests you, detect changes from the previous check, and much more. The Filters page is one of the key areas of Simon.The Service page is where you choose what to check and enter the URL or whatever other information it needs.The Options page enables you to specify how often to check the test (when the previous check was successful or failed), and other useful options.
 The Name page contains fields to name the test and write a description of it. In Edit mode, the Info pane has lots of options to help you configure each test, conveniently arranged on multiple pages: It includes an Edit button to enable modifying the test, which toggles to Done when editing to switch back to the summary. It shows a summary of the test click the heading for each line of the summary to jump right to that page.
The Name page contains fields to name the test and write a description of it. In Edit mode, the Info pane has lots of options to help you configure each test, conveniently arranged on multiple pages: It includes an Edit button to enable modifying the test, which toggles to Done when editing to switch back to the summary. It shows a summary of the test click the heading for each line of the summary to jump right to that page. 
It is accessed when the Tests list is active. So how do you tell Simon what to monitor? That's where the Test Info pane comes in.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
